Living well with diabetes as a senior is entirely possible when you take proactive steps. This guide empowers you with practical, actionable strategies for managing your condition effectively. You gain control over your health through informed choices about diet, exercise, and consistent monitoring. Embracing these habits helps you maintain a vibrant, active lifestyle.

Understanding Diabetes in Later Life
Diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes, often becomes more common as you age. Your body undergoes changes that can affect how it processes glucose, leading to higher `blood sugar` levels. Recognizing these age-related factors helps you tailor your management approach. Nearly 29% of people over 65 have diabetes, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), highlighting its prevalence in the `senior diabetes` population.
Managing diabetes in your senior years focuses on preventing complications and maintaining your quality of life. This means understanding your diagnosis, its implications, and the role you play in its daily management. Your healthcare provider helps you set personalized `blood sugar` targets and develop a comprehensive plan. Education is your first line of defense, equipping you to make informed decisions daily.
Many factors contribute to diabetes risk in seniors. These include genetics, lifestyle choices, and other health conditions. For example, conditions like high blood pressure or high cholesterol can increase your risk and complicate diabetes management. Discuss your full health history with your doctor to ensure a holistic approach to your care.

Crafting Your Diabetes-Friendly Diet Plan
What is the best `diet plan` for diabetic seniors? A balanced, consistent eating pattern forms the cornerstone of effective `senior diabetes` management. Your diet directly impacts your `blood sugar` levels, weight, and overall health. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods to stabilize your glucose and provide essential nutrients. This helps prevent sudden spikes and drops, maintaining more consistent energy levels throughout your day.
Consider these key principles for your diabetes `diet plan`:
- Emphasize Whole Foods: Prioritize vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods offer fiber, vitamins, and minerals without excess sugar or unhealthy fats.
- Portion Control: Pay attention to serving sizes. Even healthy foods can elevate `blood sugar` if consumed in large quantities. Use smaller plates or measuring cups to guide your portions.
- Regular Meal Times: Eat meals and snacks at consistent times each day. This helps regulate `blood sugar` and prevents extreme hunger, which can lead to overeating.
- Limit Processed Sugars and Refined Carbs: Avoid sugary drinks, desserts, and white breads. These cause rapid `blood sugar` increases. Choose complex carbohydrates, such as brown rice and oats, instead.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Water supports overall health and helps your body process glucose effectively.
Consulting a registered dietitian nutritionist (RDN) is invaluable. An RDN works with you to create a personalized `diet plan` that fits your tastes, cultural background, and medical needs. They also help you navigate food labels and understand the glycemic index of different foods. The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics provides resources for finding qualified professionals. Find an RDN through the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics to create your tailored eating strategy.

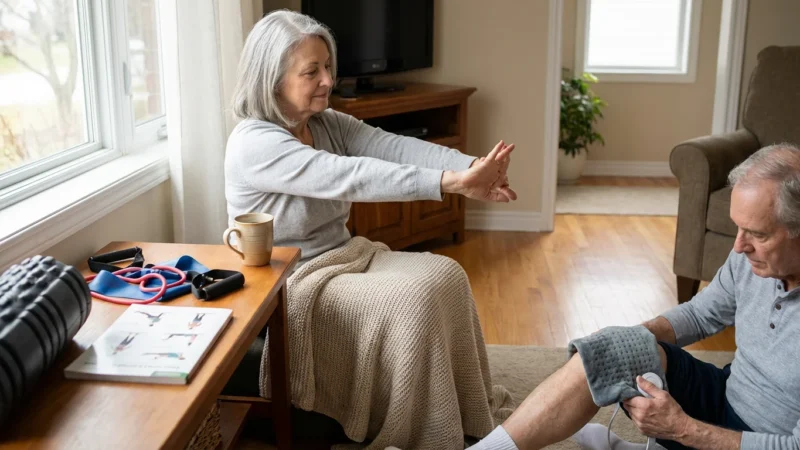
Effective Exercise for Blood Sugar Control
Physical activity plays a crucial role in managing `senior diabetes`. Regular exercise helps your body use insulin more efficiently, which in turn lowers `blood sugar` levels. It also contributes to weight management, improves cardiovascular health, and boosts your mood. Before starting any new exercise routine, talk to your doctor to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your health status.
Incorporate a mix of aerobic and strength training exercises into your weekly routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, spread throughout the week. You can break this into 30-minute sessions most days. Additionally, include muscle-strengthening activities at least two days a week.
Here are examples of exercises beneficial for `senior diabetes` management:
- Brisk Walking: An accessible and effective aerobic exercise. Start with shorter distances and gradually increase your pace and duration.
- Swimming or Water Aerobics: Low-impact options that are gentle on joints while providing excellent cardiovascular benefits.
- Cycling (Stationary or Outdoor): Builds leg strength and endurance. Adjust resistance to match your fitness level.
- Chair Yoga or Tai Chi: Improves flexibility, balance, and reduces stress, all important for overall wellness.
- Resistance Band Exercises: Excellent for building muscle strength without heavy weights. Focus on major muscle groups.
- Dancing: A fun way to get your heart rate up and improve coordination.
Remember to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. Listen to your body and take rest days when needed. Always carry a small snack or glucose tablets if you are on insulin or certain medications, in case of low `blood sugar`. Staying active is a powerful tool in your `senior diabetes` management strategy.
“Take care of your body. It’s the only place you have to live.” — Jim Rohn
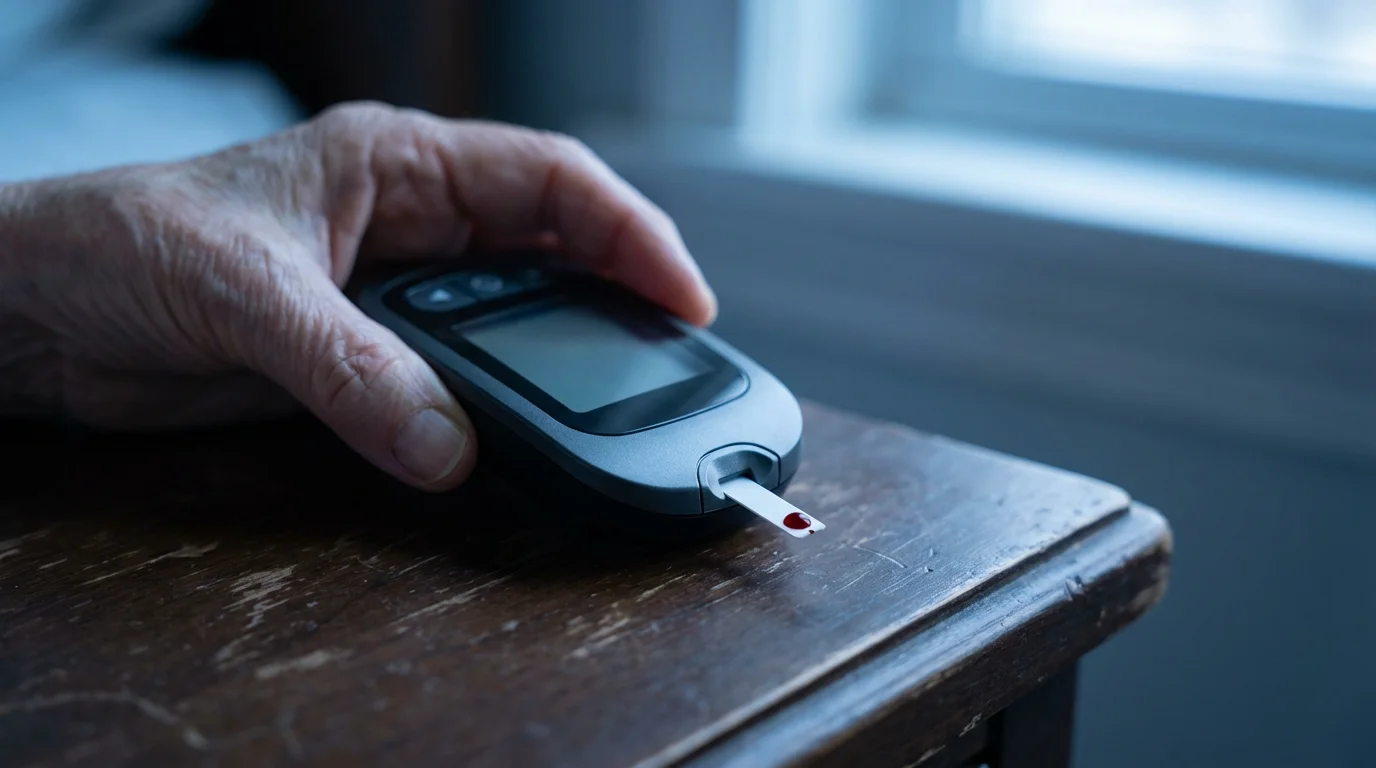

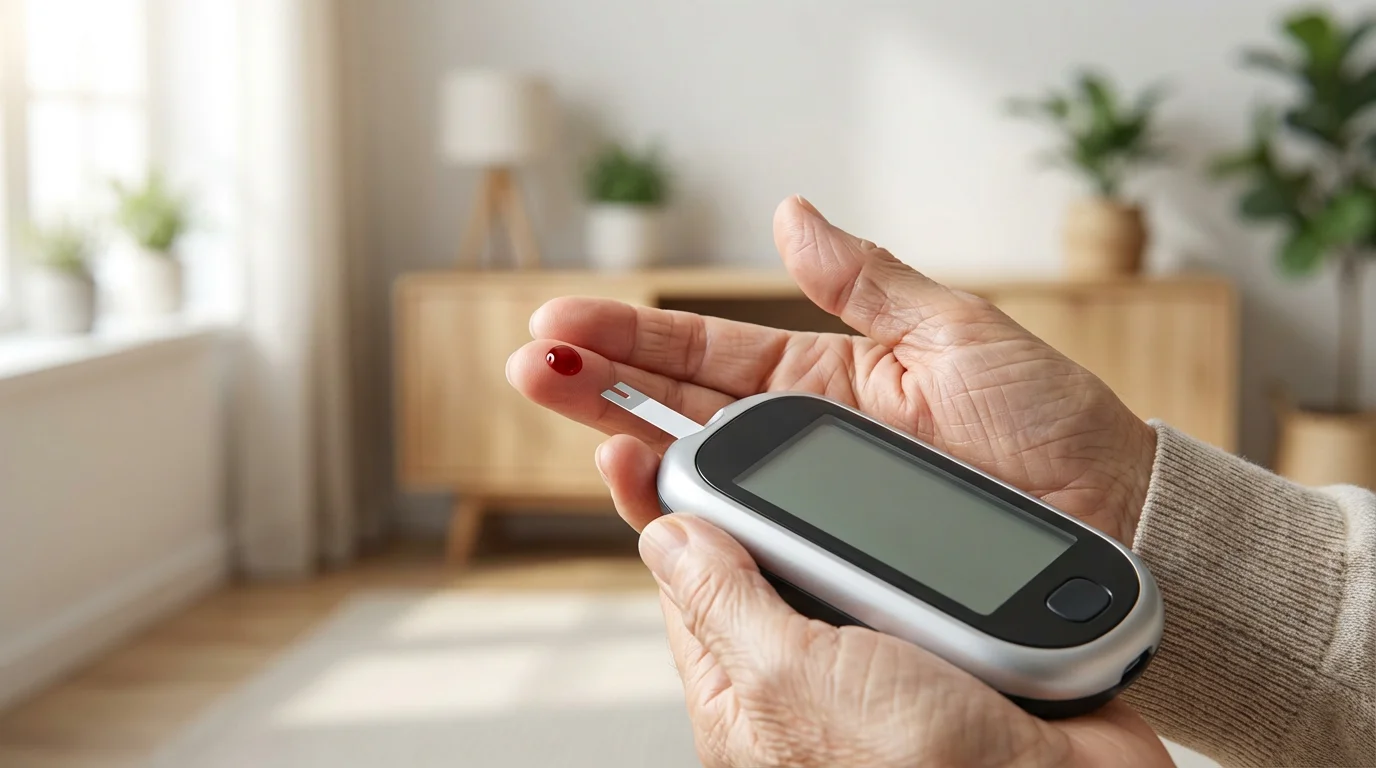
Monitoring Your Blood Sugar Effectively
Consistent `blood sugar` monitoring provides vital information for managing your `senior diabetes`. It shows you how your diet, exercise, and medications affect your glucose levels. This immediate feedback empowers you to make adjustments and work with your healthcare team for optimal control. Regular monitoring helps prevent both dangerously high and dangerously low `blood sugar`.
Your doctor will advise you on how often to check your `blood sugar`. This might be several times a day, or less frequently, depending on your type of diabetes, medications, and overall health. Use a glucometer correctly and record your readings. Many modern glucometers offer memory functions or can sync with apps, simplifying the tracking process.
Key aspects of effective `blood sugar` monitoring:
- Understand Your Targets: Discuss with your doctor what your ideal `blood sugar` ranges are before meals, after meals, and at bedtime. These targets are personalized.
- Consistent Testing: Follow your prescribed testing schedule. Missing tests means missing crucial data points that inform your management.
- Record Keeping: Keep a log of your `blood sugar` readings, noting the time, any relevant food intake, and activity. This helps identify patterns.
- HbA1c Tests: Your doctor will periodically order an HbA1c test, which provides an average of your `blood sugar` levels over the past 2-3 months. This gives a broader picture of your control.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Some seniors may benefit from CGMs, which provide real-time `blood sugar` readings without frequent finger pricks. Discuss this option with your doctor.
Understanding your `blood sugar` trends allows you and your healthcare provider to fine-tune your `diet plan`, adjust medication dosages, and optimize your exercise routine. Proactive monitoring keeps you ahead of potential issues.
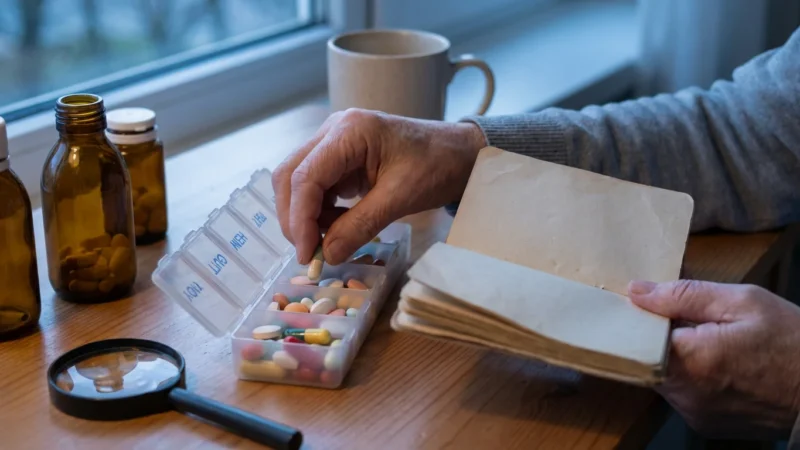
Medication Management and Adherence
Many seniors with diabetes require medication to help manage their `blood sugar`. This might include oral medications, insulin, or other injectable drugs. Taking your medications exactly as prescribed is crucial for controlling your `blood sugar` and preventing complications. Adherence to your medication regimen forms a critical pillar of effective `senior diabetes` management.
It is common for seniors to take multiple medications for various health conditions. This polypharmacy can make managing your diabetes medications more complex. Develop a system to help you remember dosages and timings.
Practical tips for medication management:
- Use a Pill Organizer: A weekly or daily pill box helps ensure you take the correct medication at the right time.
- Set Reminders: Use alarms on your phone, a watch, or a simple reminder note to prompt you for doses.
- Understand Each Medication: Know what each drug is for, its dosage, and potential side effects. Ask your pharmacist or doctor if you have questions.
- Review Medications Regularly: Schedule regular medication reviews with your doctor or pharmacist. They can identify potential interactions or adjust dosages if your health status changes.
- Never Self-Adjust: Do not change your medication dosage or stop taking a drug without first consulting your doctor.
Exploring prescription drug savings programs can also ease the financial burden of managing diabetes. Medicare Part D plans cover prescription drugs, and you can compare plans on Medicare.gov to find one that best fits your needs. Discuss generic alternatives with your doctor, as these often provide significant savings without compromising effectiveness.

Preventing Complications: A Proactive Approach
Long-term `senior diabetes` management centers on preventing complications that can affect your eyes, kidneys, nerves, and heart. High `blood sugar` levels over time damage small blood vessels and nerves, leading to serious health issues. Taking proactive steps significantly reduces your risk and preserves your quality of life. Consistent `blood sugar` control is your most powerful defense.
You can take several key steps to prevent diabetes complications:
- Regular Eye Exams: Schedule comprehensive dilated eye exams annually. Diabetes can lead to conditions like diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and cataracts. Early detection helps preserve your vision.
- Kidney Health Checks: Your doctor will perform regular urine tests to check for protein (a sign of kidney damage) and `blood sugar` tests to monitor kidney function. Maintain good `blood sugar` and blood pressure control to protect your kidneys.
- Foot Care: Inspect your feet daily for cuts, sores, blisters, or swelling. Nerve damage (neuropathy) can reduce sensation, making injuries unnoticed. Wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes. See a podiatrist regularly.
- Heart Health: Diabetes increases your risk of heart disease and stroke. Manage your `blood sugar`, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. Follow a heart-healthy `diet plan` and engage in regular physical activity. The American Heart Association offers valuable resources for maintaining heart health. Visit the American Heart Association for more on diabetes and heart health.
- Nerve Care: Good `blood sugar` control minimizes nerve damage. Report any tingling, numbness, or pain to your doctor.
- Dental Health: Diabetes increases your risk of gum disease. Maintain good oral hygiene and schedule regular dental check-ups.
Working closely with your healthcare team to monitor these areas ensures you address any potential issues early. Your diligence in managing your `blood sugar`, `diet plan`, and exercise habits directly impacts your long-term health outcomes.
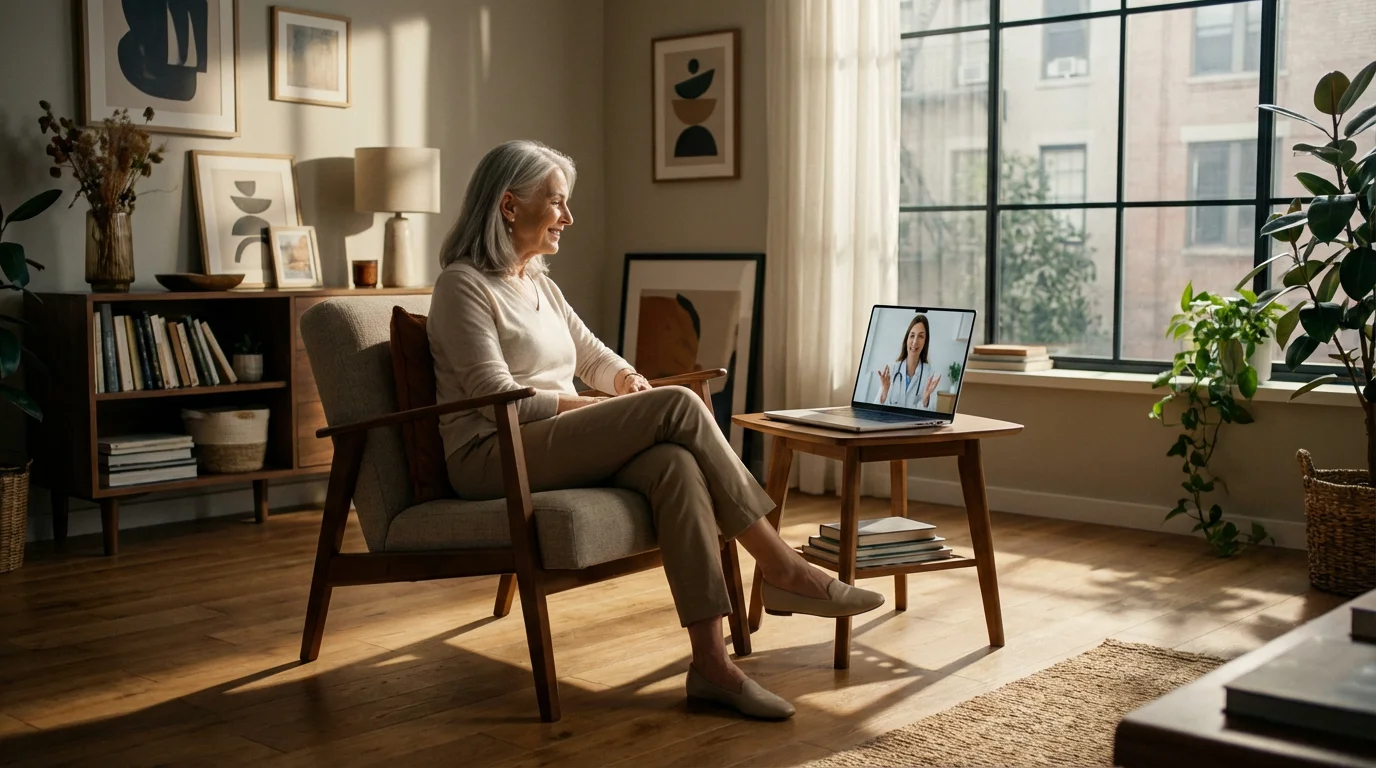

The Role of Telehealth and Your Healthcare Team
Effectively managing `senior diabetes` relies on a strong partnership with your healthcare team. This team often includes your primary care physician, an endocrinologist, a registered dietitian, a certified diabetes educator, and potentially a podiatrist or ophthalmologist. Each specialist contributes to a holistic approach to your care. Open communication with each team member is essential.
Telehealth has emerged as a convenient and effective way to access diabetes care, especially for seniors. Virtual appointments allow you to consult with your doctors and other specialists from the comfort of your home. This reduces travel time and potential exposure to illness, making consistent care more accessible.
Benefits of utilizing telehealth for diabetes management include:
- Convenience: Attend appointments without leaving your home, saving time and reducing transportation stress.
- Regular Check-ins: Easily schedule follow-up appointments to monitor `blood sugar` trends, adjust medications, or discuss your `diet plan`.
- Access to Specialists: Connect with specialists who might not be locally available, such as endocrinologists or dietitians.
- Remote Monitoring: Some telehealth platforms integrate with devices like continuous glucose monitors, allowing your doctor to review your data remotely.
- Education and Support: Participate in virtual diabetes education classes or support groups.
Ensure your healthcare providers are aware of all your medications and current health conditions. Do not hesitate to ask questions or express concerns during your appointments, whether in person or via telehealth. Your active participation is a key factor in successful `senior diabetes` management.

When to See a Doctor About Your Diabetes
Knowing when to seek medical attention for your diabetes is critical for your safety and well-being. While regular check-ups are routine, certain symptoms or `blood sugar` readings warrant immediate consultation with your doctor. Always prioritize prompt communication with your healthcare provider.
Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Persistently High Blood Sugar: If your `blood sugar` readings consistently exceed your target range despite following your `diet plan` and medication schedule.
- Frequent Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia): Symptoms like shakiness, confusion, dizziness, excessive sweating, or rapid heartbeat. This requires immediate action and medical review.
- New or Worsening Symptoms: Any new vision changes, numbness or tingling in your hands or feet, unhealing sores, or increased thirst and urination.
- Signs of Infection: Fever, chills, redness, swelling, or pus from a wound, especially on your feet. Seniors with diabetes are more susceptible to infections.
- Unexplained Weight Loss or Gain: Significant changes in weight without intentional `diet plan` or lifestyle alterations.
- Medication Side Effects: If you experience severe or concerning side effects from your diabetes medications.
In case of a severe emergency, such as extreme confusion, loss of consciousness, or severe chest pain, call 911 immediately. Never delay seeking help for urgent symptoms. Your doctor helps you differentiate between minor fluctuations and serious issues, guiding you to make the best health decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of managing diabetes as a senior citizen?
The primary goal involves maintaining stable `blood sugar` levels to prevent complications, preserve organ function, and ensure a high quality of life. This includes managing your `diet plan`, incorporating physical activity, and adhering to medication schedules.
How often should a senior with diabetes check their blood sugar?
The frequency of `blood sugar` monitoring varies based on your type of diabetes, medications, and your doctor’s recommendations. Some seniors may need to check several times a day, while others test less frequently. Always follow your healthcare provider’s specific instructions.
Can seniors reverse type 2 diabetes through diet and exercise?
While remission of type 2 diabetes is possible for some individuals, particularly with significant lifestyle changes early on, it is not a universal outcome. Seniors can achieve excellent `blood sugar` control and improve their health significantly through consistent diet and exercise, often reducing medication needs. Always discuss your specific goals and progress with your doctor.
What are the safest exercises for diabetic seniors?
Safest exercises include brisk walking, swimming, water aerobics, cycling, chair yoga, and tai chi. Always consult your doctor before starting any new exercise program to ensure it is appropriate for your individual health status and any existing conditions.
How can seniors save money on prescription diabetes medications?
Seniors can save on prescription medications by utilizing Medicare Part D plans, exploring generic medication options with their doctor, and investigating patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies. Comparing plans annually on Medicare.gov helps find cost-effective coverage.
Why is foot care so important for seniors with diabetes?
Diabetes can lead to nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor circulation, making seniors more prone to foot injuries and infections that heal slowly. Daily foot inspections, proper footwear, and regular visits to a podiatrist are essential to prevent serious complications like ulcers and amputations.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. The information provided is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your diet, exercise routine, medications, or health regimen. If you’re experiencing a medical emergency, call 911 immediately.









Leave a Reply